Good News From Sumatra

March 19, 2020
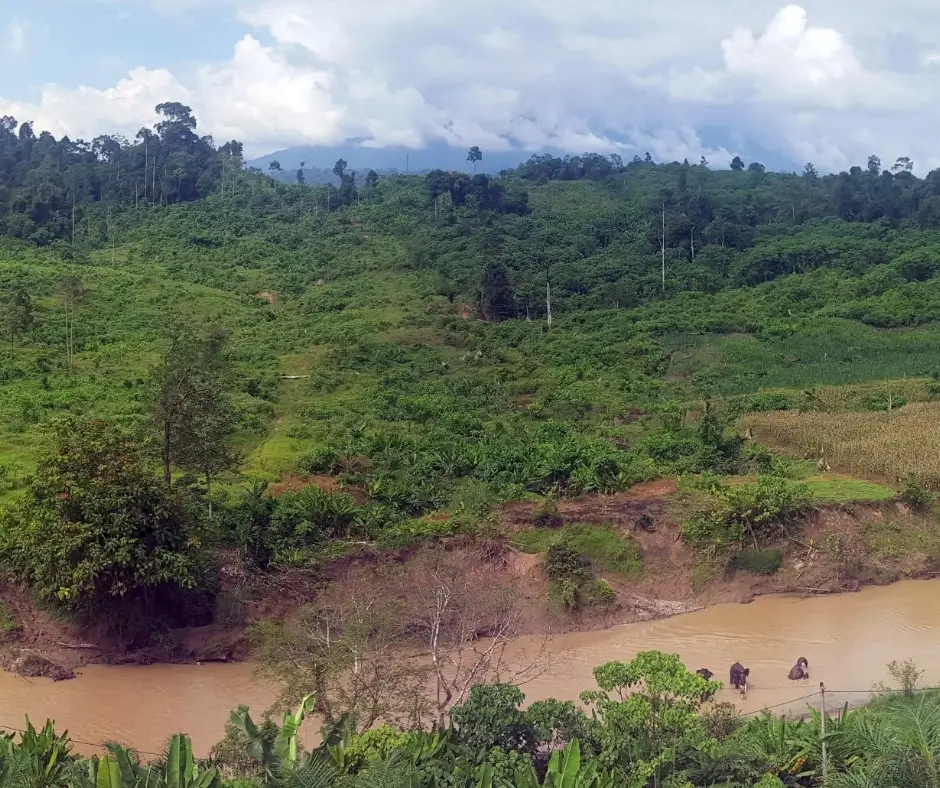
We are pleased to announce that we have funded a significant land acquisition for biodiversity conservation in the Leuser Ecosystem of Sumatra.
Saving Nature expands Forest Protections in Sumatra
Working in partnership with Forum Konservasi Leuser (FKL), a leading NGO on the frontlines of conservation efforts in the region.
The newly acquired 208-acre parcel is part of a larger initiative to build a wildlife corridor in Sumatra to combat the loss of habitat, re-establish elephant migration routes, and build a buffer against poachers. This latest addition nearly doubles to size of the existing corridor, significantly narrowing the gap between two large forest blocks in the northeast Leuser Ecosystem. Restoration of the corridor with native trees will sequester over 2,150 tons of carbon dioxide each year to combat climate change.
Saving Nature launched this visionary 3-year project in 2018. Our long-term goal is to create a 1,260-acre wildlife corridor that strategically leverages established conservation protections for a great diversity of flora and fauna. Our plan is to connect a 13,500-acre area recently designated by the Indonesian government as an elephant conservation area with over 740,000 acres of protected forest.
Acquisition of the land was made possible through the generosity of individuals committed to restoring critical habitat for threatened and endangered species. Consistent with our operating philosophy of building local capacity for long-term success, Saving Nature has partnered with Forum Konservasi Leuser (FKL), a leading NGO on the frontlines of conservation efforts in the region. Together, we are working to create a sustainable for the unique biodiversity of Sumatra.
"Together with Forum Konservasi Leuser, we are establishing an important wildlife corridor in Leuser that will help ensure that threatened and endangered species can move freely, preventing populations from becoming isolated. Without this corridor, increasing human development will further sever the connections among forest blocks, impeding wildlife movement and undermining their resiliency. The new corridor will rebuild habitat and sequester carbon for decades to come."
Stuart Pimm, President of Saving Nature Tweet
sumatra's wildlife needS A refuge
Help build a connection to the future for the wildlife of Leuser. Take a stand for their last refuge by rescuing this vanishing ecosystem, preventing the loss of biodiversity, and building resilience to fight the impacts of climate change.
All Conservation is Local

March 4, 2020
All Conservation is Local
A FILM BY JAMES ROBINSON
Camera Trapping Challenges

March 4, 2020
Camera Trapping Challenges
A FILM BY JAMES ROBINSON and JACOB LEVINE
The World’s Great Forests You’ve Never Heard Of

February 5, 2020
Andrew Schiffer takes a global tour of the world’s greatest forests and makes the case for taking “remote ownership” of their protection. His call to action encourages people to learn more about the world around us and get involved in saving these special places.
The World's Great Forests You've Never Heard Of
by Andrew Schiffer
With limited funding and climate change upon us, conservationists must decide which forests to focus on and preserve. Although every forest possesses its own value, in order to prioritize funding, it is critical for our humanity to identify ‘biodiversity hotspots’ where the highest concentrations of endemic species are facing the largest loss of habitat.
I have narrowed down the candidates to five particularly vital hotspots: Brazil’s Atlantic Forest, Choc/Darien/Western Ecuador, Western Ghats/Sri Lanka, Indo-Burma, and the Tropical Andes.
These hot spots all contain a treasure trove of critical, different wildlife and plant species. In addition, many of them are brimming with life endemic only to the area. In learning more about these crucial hotspots, specifically about the statistical number of species that inhabits each area, we will learn some important facts that are compelling for each of us to take “remote ownership” and learn more.
These numbers are more shocking when “In contrast, the United States and Canada, with an expanse 8.8 times larger than the 25 hotspots combined, have only two endemic families of plants.” Although we are providing a brief overview of the importance of conserving each forest, there is still a lot to learn and we encourage you to explore the Saving Nature website to learn more and hopefully be inspired to carry out some research on your own!
South America
First off, Brazil’s Atlantic Forest makes up such a huge amount of the Earth’s surface that it contains two of the world’s largest cities: Rio de Janeiro and Sao Paulo. The forest spans over 3,000 km along the coast of Brazil and into Paraguay and Argentina. The forest is home to the biggest big cat in South America, the jaguar, as well as two indigenous tribes: The Tupi and the Guarani. In 1832, Charles Darwin explored the forest during his expedition on the Beagle. The forest is also home to over 2% of both the world’s endemic plants and vertebrates. It boasts the third largest number of endemic plants in the world, topping 8,000. However, in the face of growing threats, the forest has recently lost all, but 7.5% of its original primary vegetation and species, threatening the very existence of the native Jaguar.
The Tropical Andes, also located in South America, stands as an equally special woodland. Holding over 20,000 endemic plants as of yet discovered; the forest has long fascinated scientists. 1,666 bird species call it their home, a number that far exceeds any other hotspot in the world. Furthermore, the Tropical Andes contains at least 2% of the total endemic plants and vertebrates worldwide. With jaw-dropping statistics such as this, as well as 6.7% of all plant species extinct, we must give it our utmost attention.
Rounding out the South America candidates, the Choco/Darien/Western Ecuador forest presents its own case for being saved, struggling to maintain the mere 4.9% of its primary vegetation that remains. Due to its isolation, the forest is particularly attractive to endemic life. This stems from the forests on the western side of the Andes having evolved entirely differently from their counterparts on the eastern side.
The numbers are quite staggering: 830 birds (85 endemic), 235 mammals (60 endemic), 210 reptiles (63 endemic), and 350 amphibian species (210 endemic). Without question, the forests are one of the primary sources of endemic life. They also contain 0.8% of the global total of endemic plants and 1.5% of the world total endemic vertebrates.
They run along the entire Columbian coast and are made up of mountains, rain forests, and coastal areas. Species include jaguars, ocelots, giant anteaters, tapirs, and tamarins. The adorable cotton-top tamarin can only be found there and could risk extinction without our immediate intervention. Such profound data compel us to consider the Choco/Darien/Western Ecuador Forest’s significance.
Tropical Asia
As we travel to the 2 million km of tropical Asia and the lowlands of the Mekong Delta in Vietnam, we find the Indo-Burma forests. With 1,170 bird species, 329 mammal species, 202 amphibian species, and 484 reptile species, these forests contain many of the world’s great animals: leaf deer, kouprey, white-eared night-herons, Mekong giant catfish, and Jullien’s golden carps to name but a few.
Nearby stretches the last of the five highlighted forests: the Western Ghats/Sri Lanka forests. The Western Ghats region of India contains more than 30% of all plant, fish, herpetofauna, bird and mammal species found in the country, yet account for less than 6% of the national land area. Once again the numbers are staggering: 528 bird species (40 endemic), 140 mammal species (38 endemic), 259 reptile species (161 endemic), 146 amphibian species (116 endemic). Species include the mountain shrew, the slender loris, the grizzled squirrel, Layard’s striped squirrel, 144 aquatic birds, the black-spined toad, the skittering frog, the Indian bullfrog, and the Malabar torrent toad.
Furthermore, these forests are home to 0.7% of the world’s endemic plant species. In 200 square kilometers, you’ll find an average of 35 species of plants found nowhere else on earth. You’ll also find 1.3% of the world’s endemic vertebrates – that’s an average of almost 6 species found only here. With only 6.8% of its primary vegetation remaining, the Western Ghats/Sri Lanka forests call out for our help.
Caring for Our Great Forests
If we do not help save these one of a kind, crucial, magical places, the world will face mass extinction, causing millions of species to die out. This will cause an alarming imbalance in our ecosystem and cause unforeseen damage to our ecosystem and our daily life as humans. While we may feel comfortably safe here now, and these magical forests may feel far away, still there is a crucial role each of us can play in saving our magical, treasured species, and in saving nature. Feel proud and be a part of this vanishing opportunity—do not stand idly by! Thankfully, and excitedly, together we can all play a critical role in saving nature. YOU HAVE MADE A GREAT FIRST START IN LEARNING MORE.
Although they are far away for many of us, these forests contain some of the most important endemic species and vegetation in the world. We need to answer the call! It is time to come together as one and explore ways to support conservation efforts. It is daunting to take on the task of conserving the world. Common questions are likely to come up: How do we get started? What are the most important places? How could my effort even make a difference? Very little information is provided to us directly about actual concrete ways to make real, effective change. It can be difficult to know how to make a real difference and ensure that your hard work will be effective. Well, not only can you make a difference, but we can help you get started today.
There are many great organizations out there. One that is particularly relevant is Saving Nature because, coincidentally, it is focused on saving the very same forests we just talked about. Go for a life-saving adventure and explore their projects. Together, we can save our planet, one forest at a time. Together, we can help zero in on helping save the most important hotspots in the world and make real, lasting beautiful change. Do not stand idly by—you can make yourself and our planet earth proud! Along with your other great qualities, you are now a proud nature-saver! If we do not act now, there will not be enough time to save these magical, critical species and our planet. Please kindly act now and help Saving Nature. Grateful for you, nature-saver!
help save the world's great forests
Saving Nature works in biodiversity hotspots around the world to prevent extinctions and fight climate change. Guided by science, using annual surveys with drones and camera traps, we show donors where the forests and species are returning.
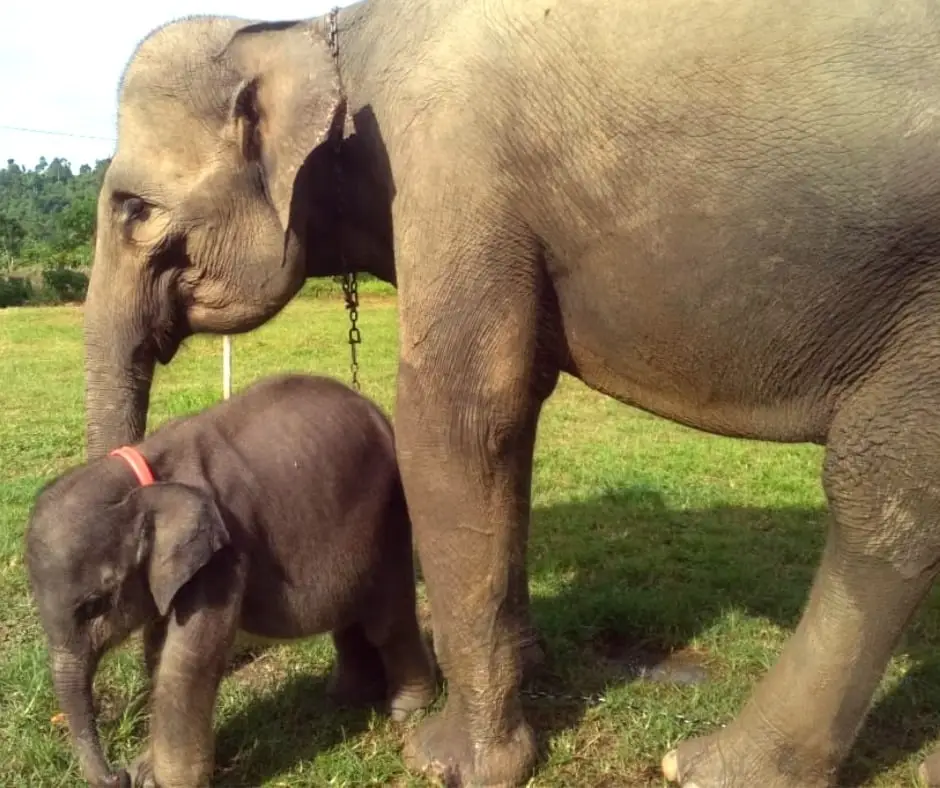
A Baby Elephant’s Rescue
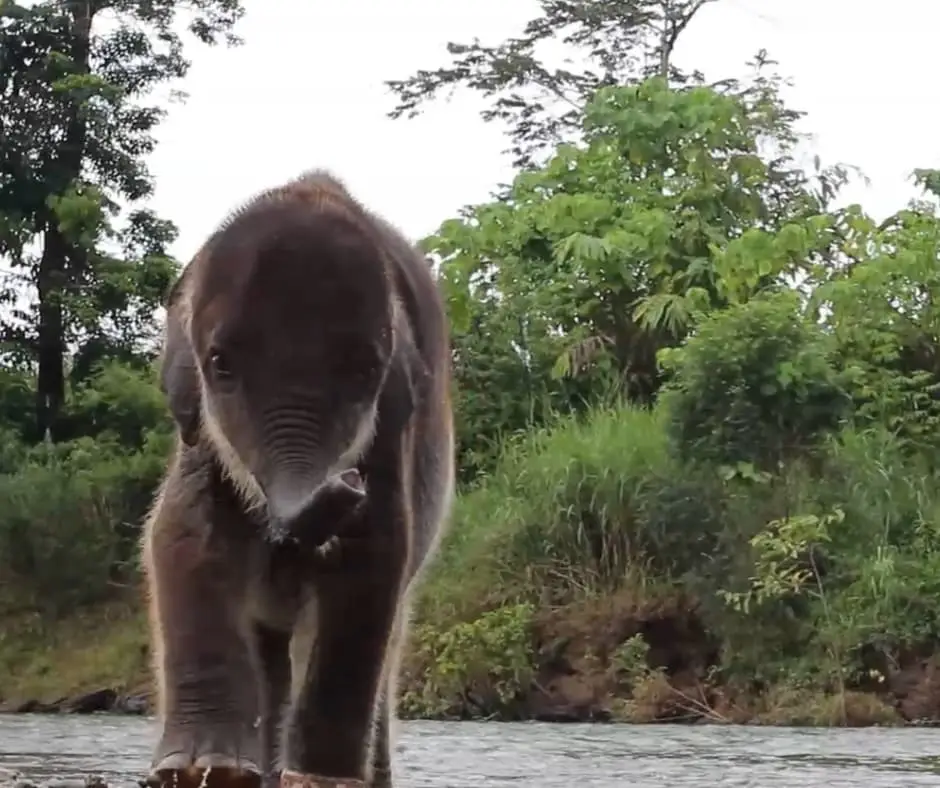

Remembering Baby Salma
Sadly, Salma died from her injuries sustained from a poacher’s snare on early on Friday, February 7, 2020. We are very saddened by this senseless loss. In sharing the news about Salma’s passing, Rudi Petra writes:
“Forgive us for failing to return you to the mother who gave birth to you, Salma. We understand your longing for your mother & best friends. We know the task of saving you is only a small part of the burden we carry. We will never give up. We will continue to fight and protect your relatives, families that are still alive and your home. We believe that one day we can save them from extinction, because only by protecting the place you play we can survive for life. Rest in peace Salma.”
We share the story of her rescue to honor those who work tirelessly to save her.
Surviving a Poacher's Snare
June 16th, 2019
by Rudi Petra, Leuser Conservation Forum (FKL)
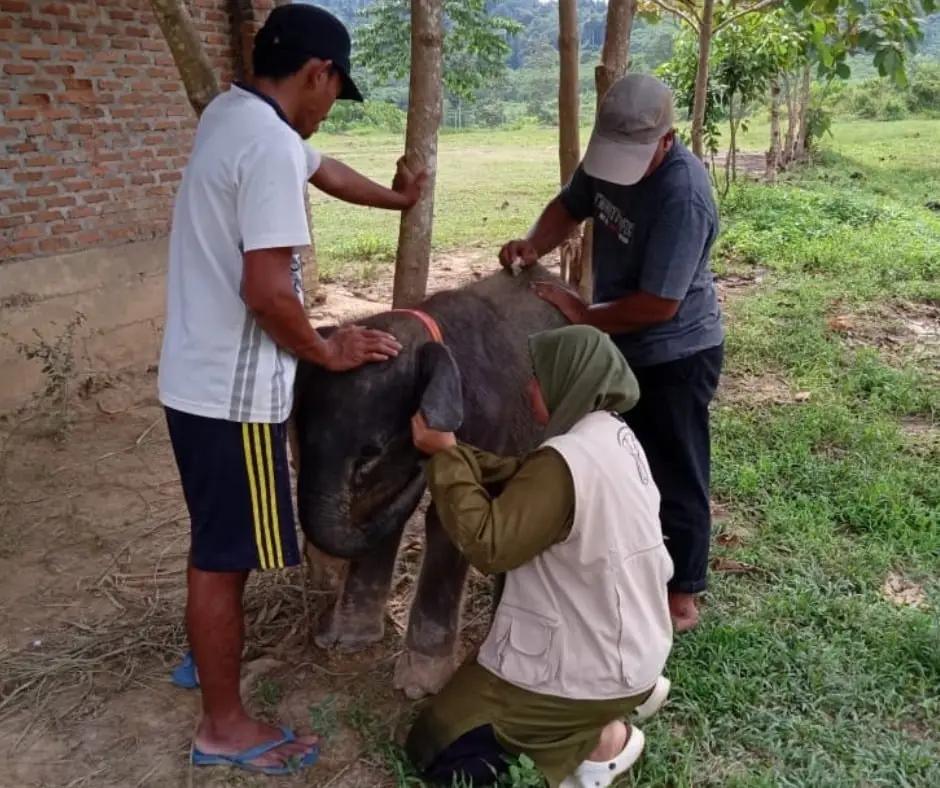
In the afternoon of June 16th, 2019, a local community member notified Leuser Conservation Forum (FKL) staff that a baby elephant had been caught by a snare on her leg at a village in rural part of Aceh Timur. At that moment, our staff contacted a veterinarian to save this baby elephant. The next day, the mission to save the elephant began.
Elephants are known to be very smart, and instinctively find a way to save injured members of their group. Working in the Leuser Ecocystem, the FKL rangers get calls about elephants bringing their injured young to an area nearby a community village – maybe hoping someone will help rescue them. Several rescue missions the FKL rangers have conducted with Aceh’s Natural Resources Conservation Agency have been very close to settlements.
A recovery team set out, following the footsteps of the baby elephant, including FKL’s Elephant Protection Team, the veterinarian, Aceh Natural Resources Conservation Agency staff, Forest Management Unit Regional 3, and local community members.
After two days of tracking the baby elephant through the forest, parts of her footsteps were lost….The team became more and more hopeless, but remained determined to continue until they found and treated the baby.
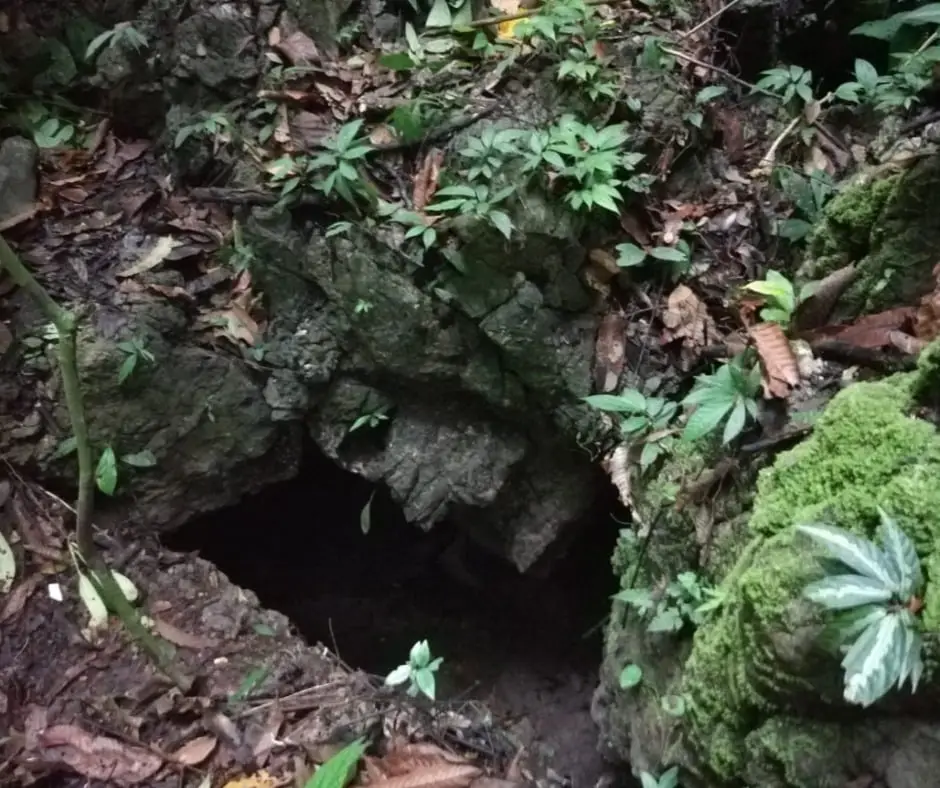
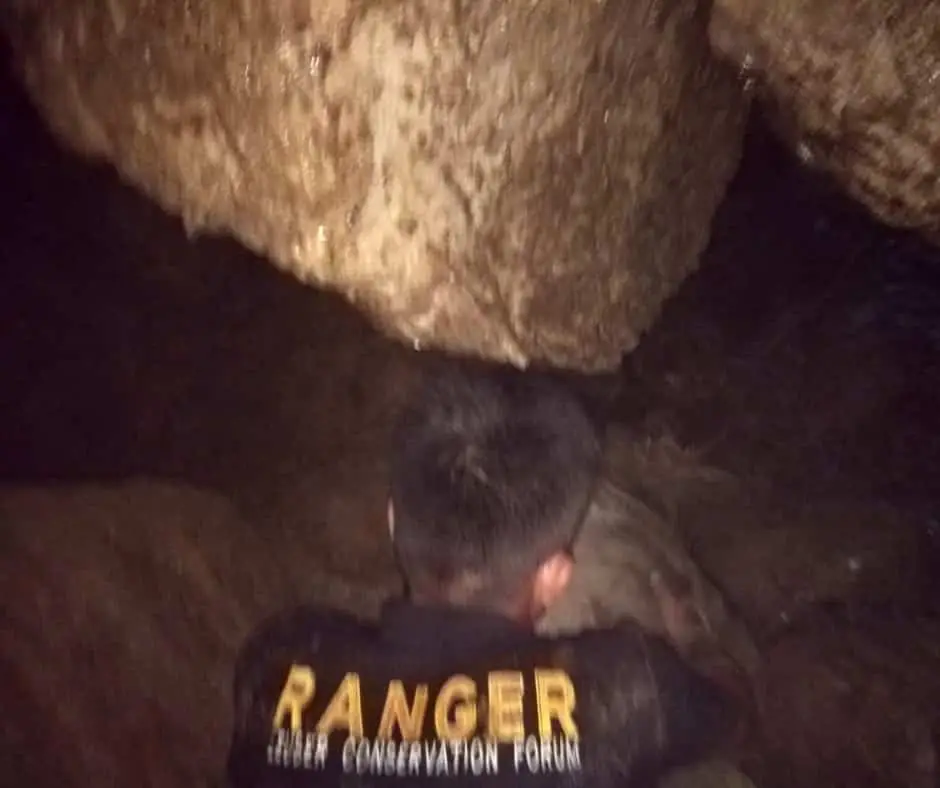
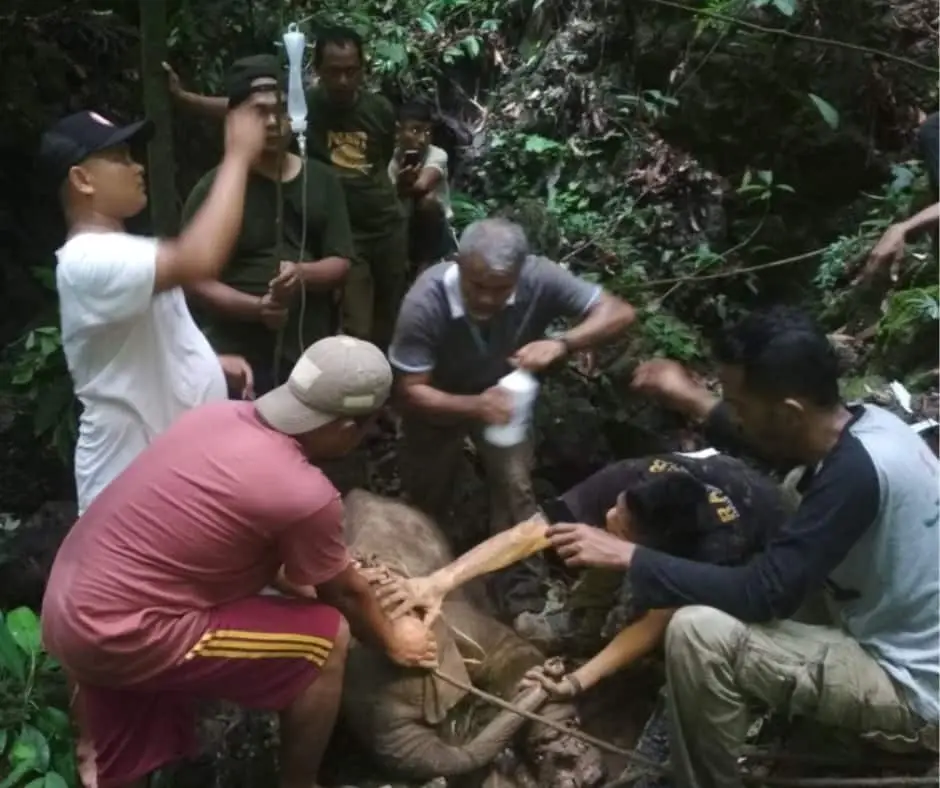
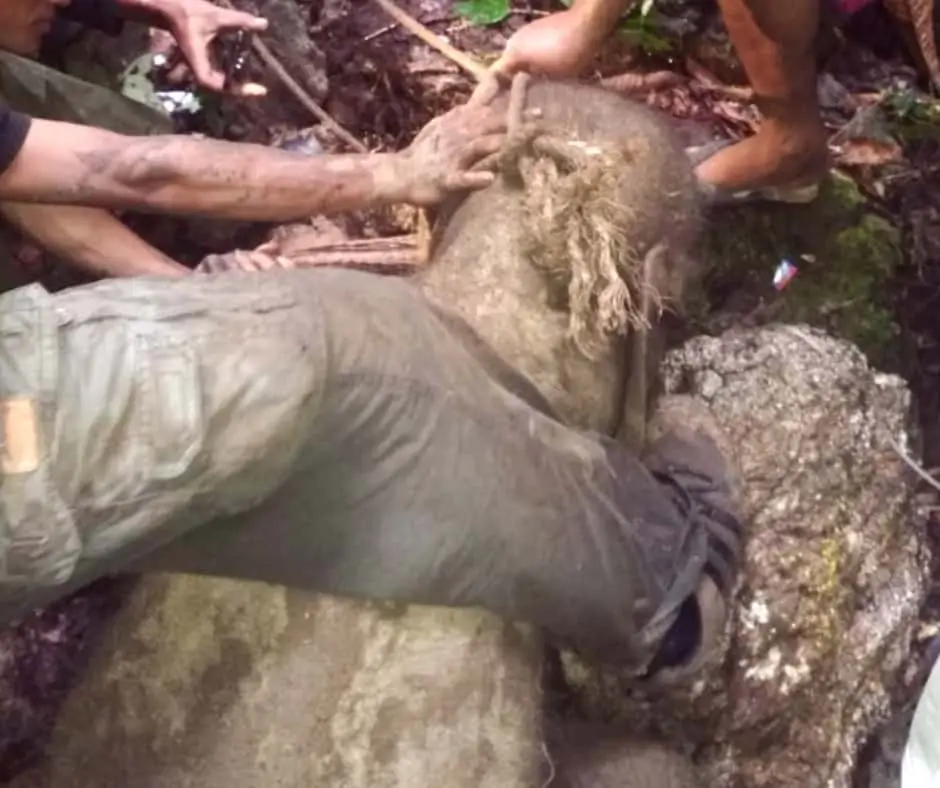





The Rescue
The team continued to search and walked until they came across a hole approximately 2 meters deep. It was inside this hole, a soft sound was heard.
The team tried to find the source of the sound, and that is where they found the weak baby elephant. Lying there distraught, maybe the elephant is no longer able to walk and wants to end her life there until her final breath.
Two members of the Elephant Patrol Team braved themselves to enter the cave to save the elephant, but her rescue was far from certain. Despite being very weak, the injured baby elephant still showed her wild nature.
With two rangers pushing below in the darkness of the cave, and another dozen using ropes from above, the team tried their very best to pull Salma from the hole.
The Frontlines of conservation
FKL’s team of 148 trained rangers patrol 13,500 square kilometers in Sumatra’s Leuser Ecosystem. In 2018, they found 843 snares set by poachers targeting protected wildlife.
In 2019, FKL’s rangers rescued 3 elephants and 1 sun bear caught in snares. They also recovered 2 hornbills and 1 orangutan from villagers intending to sell them on the black market.
Sumatran elephants, rhinos, tigers, pangolins, helmeted hornbills, and orangutans are all listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List. Their populations are declining worldwide due to poaching and habitat loss. As they disappear from other forests, the survivors face even more pressures. International poachers move into the last places where supply can be found for body parts for the Chinese black market.
Poaching is rising at an alarming rate in the last of Sumatra’s forests, with an influx of hunters from Central Sumatra and other Asian countries targeting elephants, rhinos, tigers, pangolins, hornbills, and wild birds.
With insatiable demand on the black market for tusks, horns, feathers, skins, and other body parts used in traditional medicine, cultural rituals, and decorative arts, species are moving closer to extinction.
The Leuser Ecosystem offers one of the last places where there is hope to rescue them from the brink of extinction. Connecting the two large remaining protected areas will help enormously. Restoring forests hinders access deeper into untouched areas. Returning failed farms and plantations to forest is vital to a sustainable future.
But time is critical in the race against the relentless demand. As the forests continue to recede, access becomes easier for poachers. Already driven to extinction in other parts of Indonesia, these vulnerable species, the last of their kind on earth, are now in the cross hairs.
In 2018, Saving Nature launched a 3-year initiative to build a wildlife corridor in Leuser to combat the loss of habitat, reestablish elephant migration routes, and build a buffer against poachers.
Our long-term goal is to connect a 5,500-ha area recently designated by the government as an elephant conservation area with nearly 300,000 ha of protected forest.
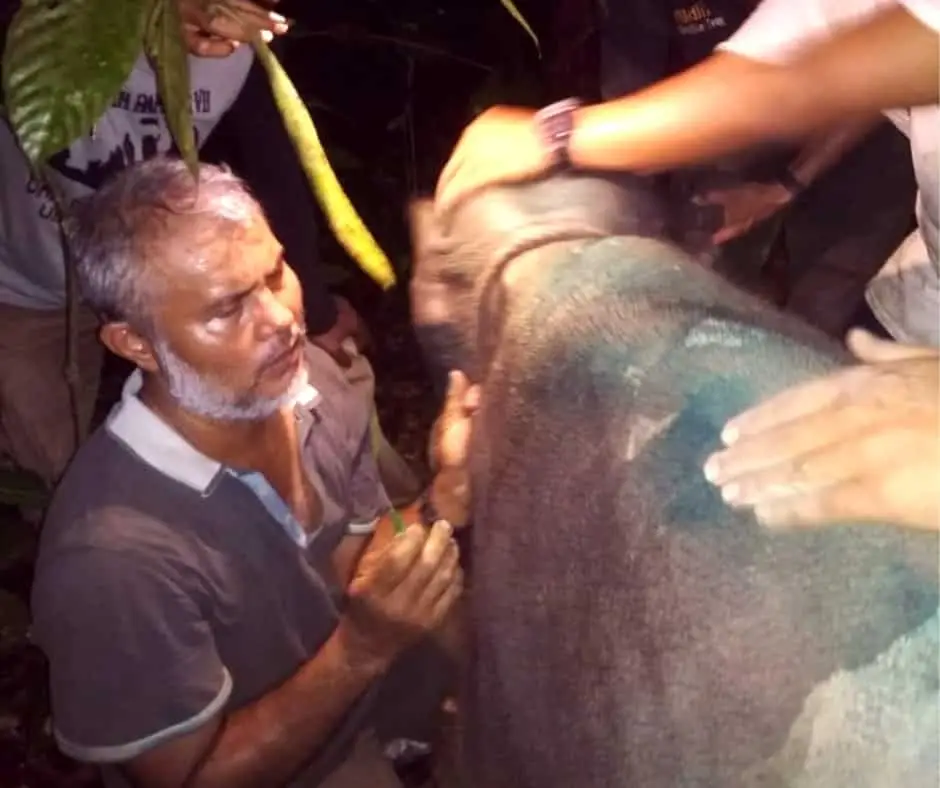
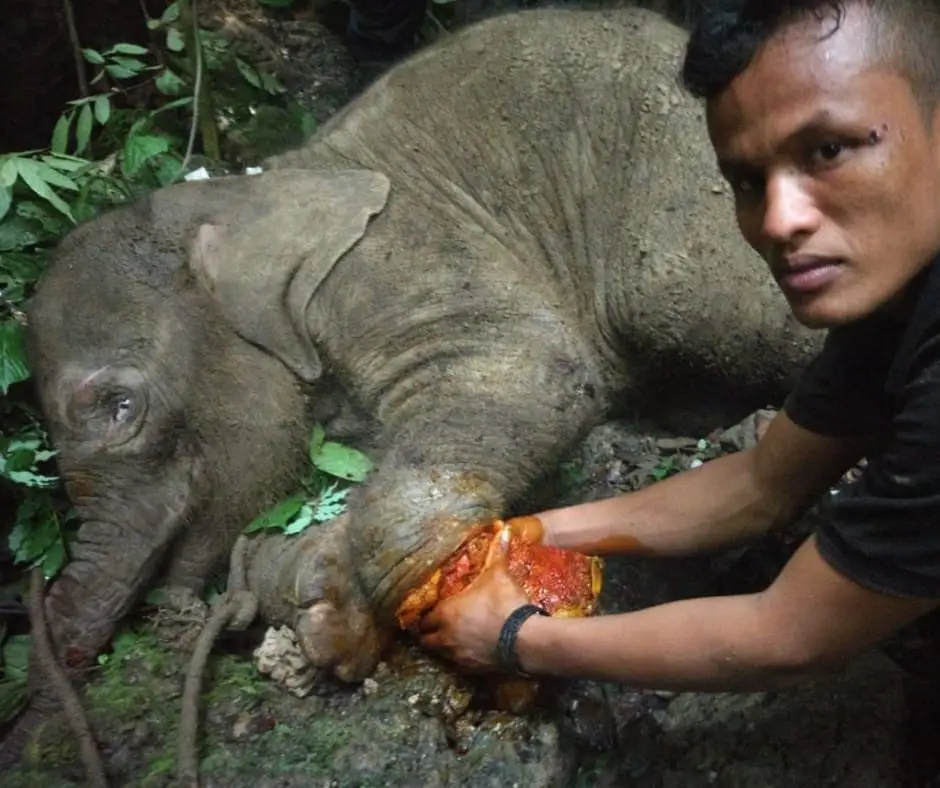
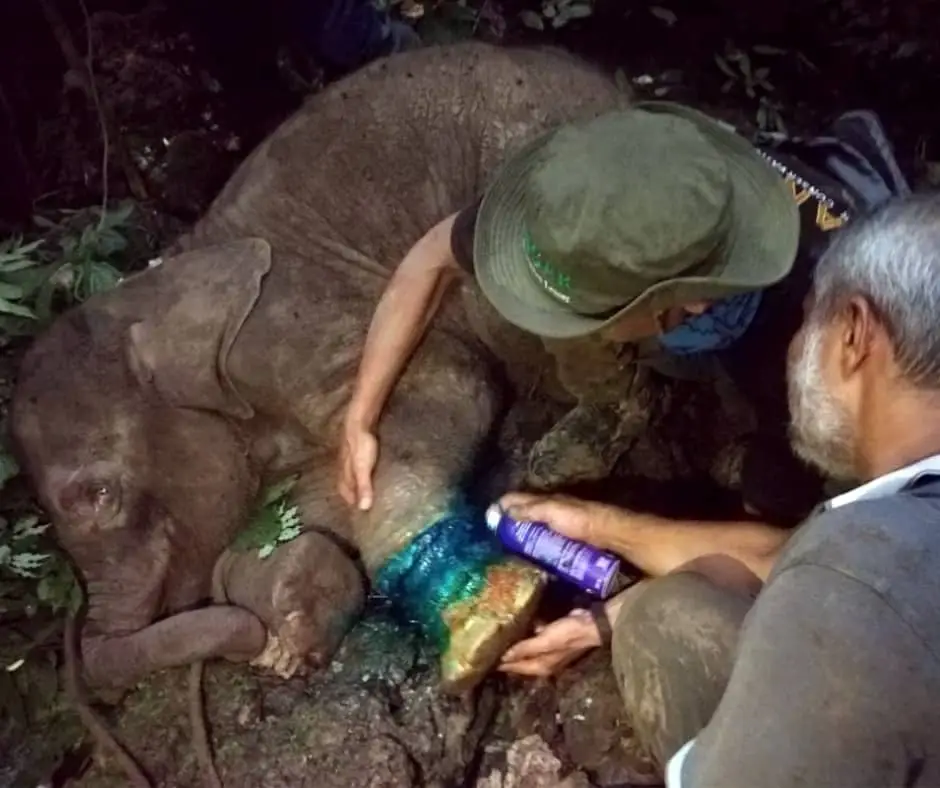
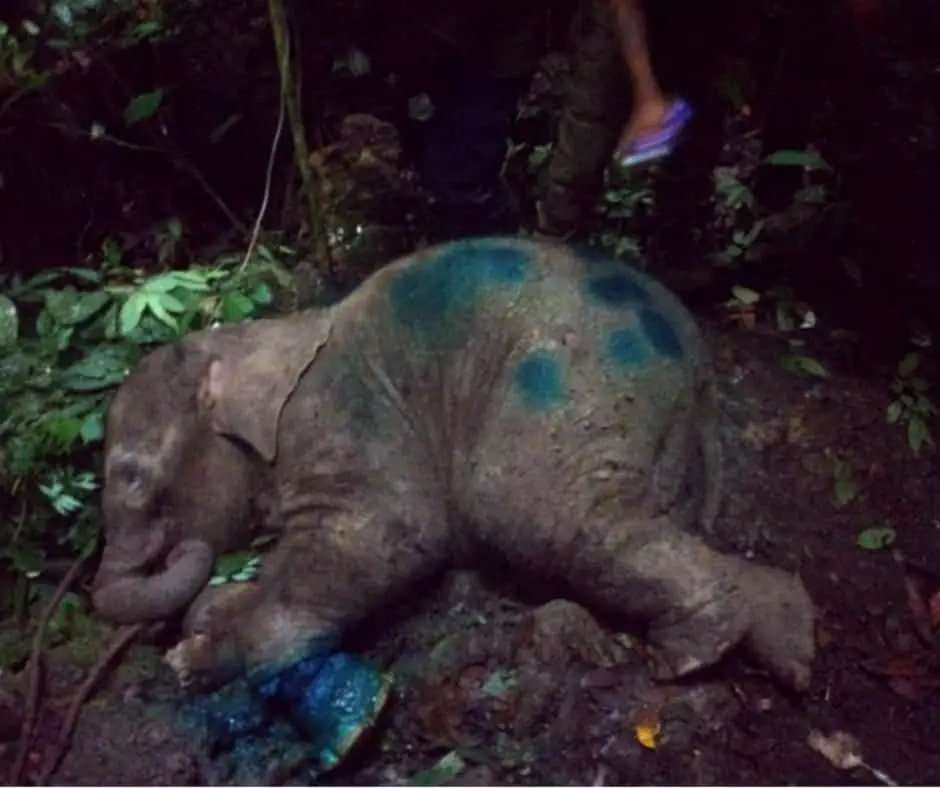




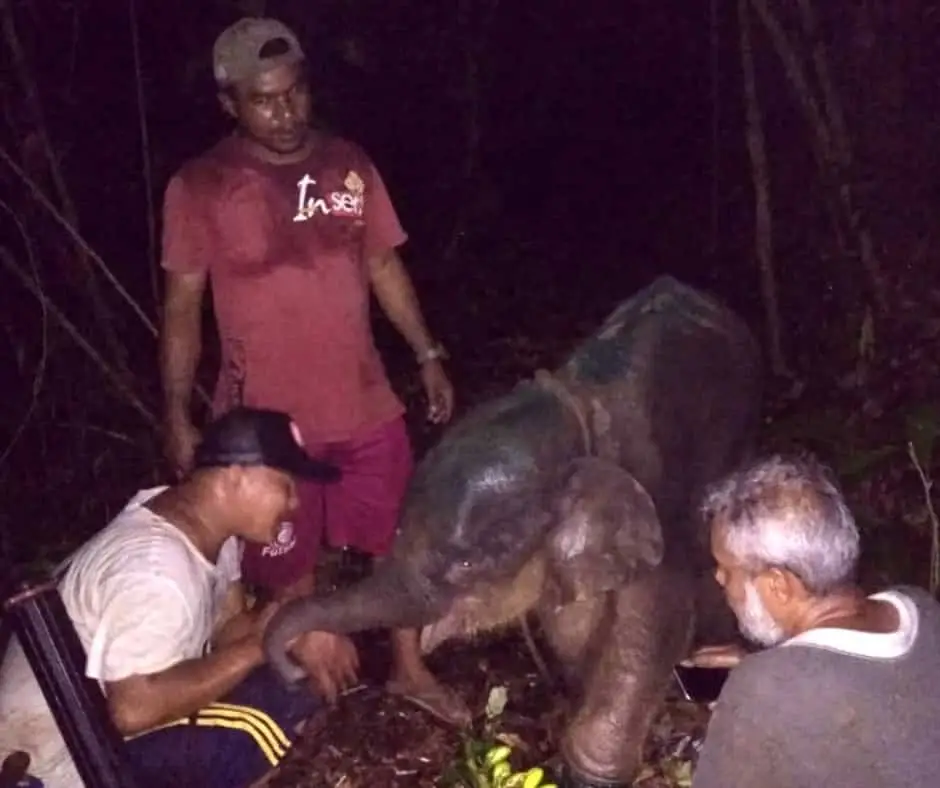
Field Triage
Finally, at 5 o’clock in the afternoon, the elephant was out of the dark cave. The veterinarian immediately injected anesthesia into the elephant, and worked to remove the snare, clean, and treat the wound.
The snare resulted in a very deep wound that came close to injuring the bones. Infection also could have killed this amazing creature.
We were very pessimistic looking at the condition of this baby elephant, but whatever the risk facing ahead, this elephant must be saved.
The Evacuation
To evacuate this little elephant was no easy feat. The location was very far from the nearest settlement. The team used a boat to go along the river to the closest settlement before it is brought on to a car.
In the middle of the night, we received help from the local community who provided the boat that is then used to bring the elephant. The elephant’s long journey began. To reach the closest settlement took 2 hours, then a 7-hour drive on land.
It was not over yet. ..
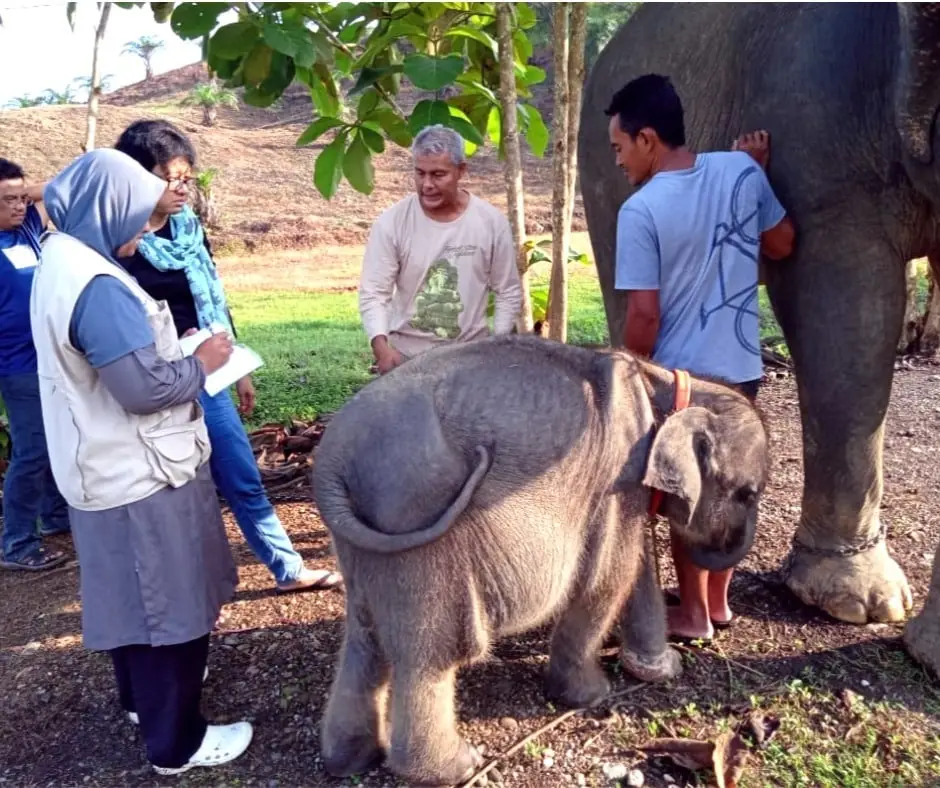
The elephant took another boat ride to reach the elephant camp, Conservation Research Unit (CRU) Serbajadi, in East Aceh. She will spend her time recovering here until she is ready to be released back in the wild to meet her family.
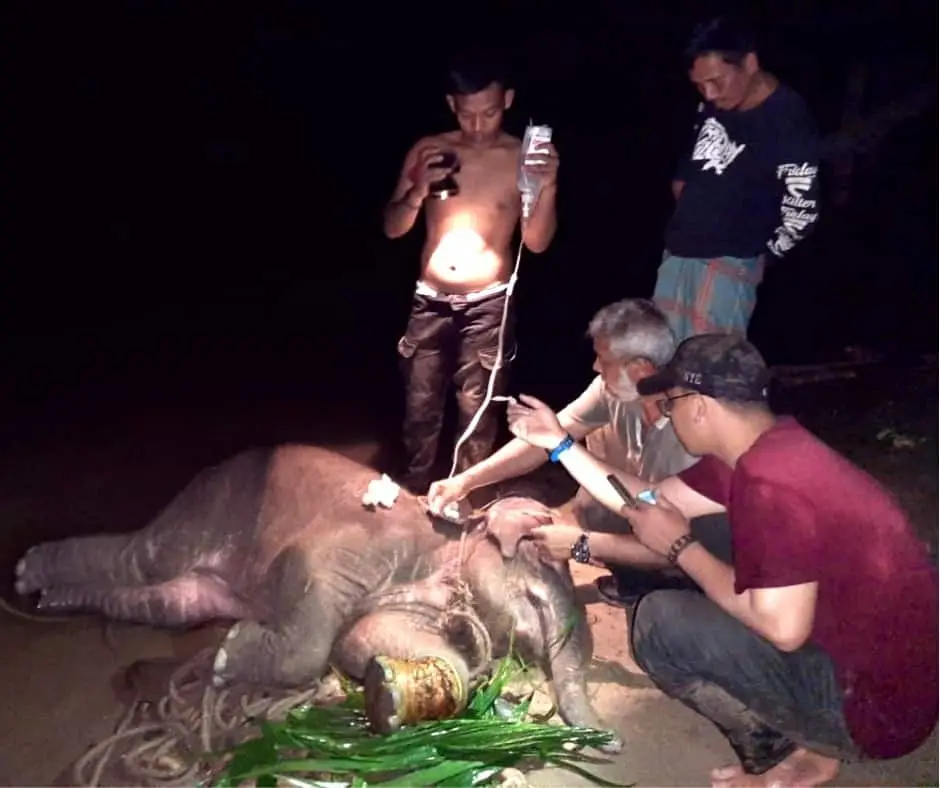
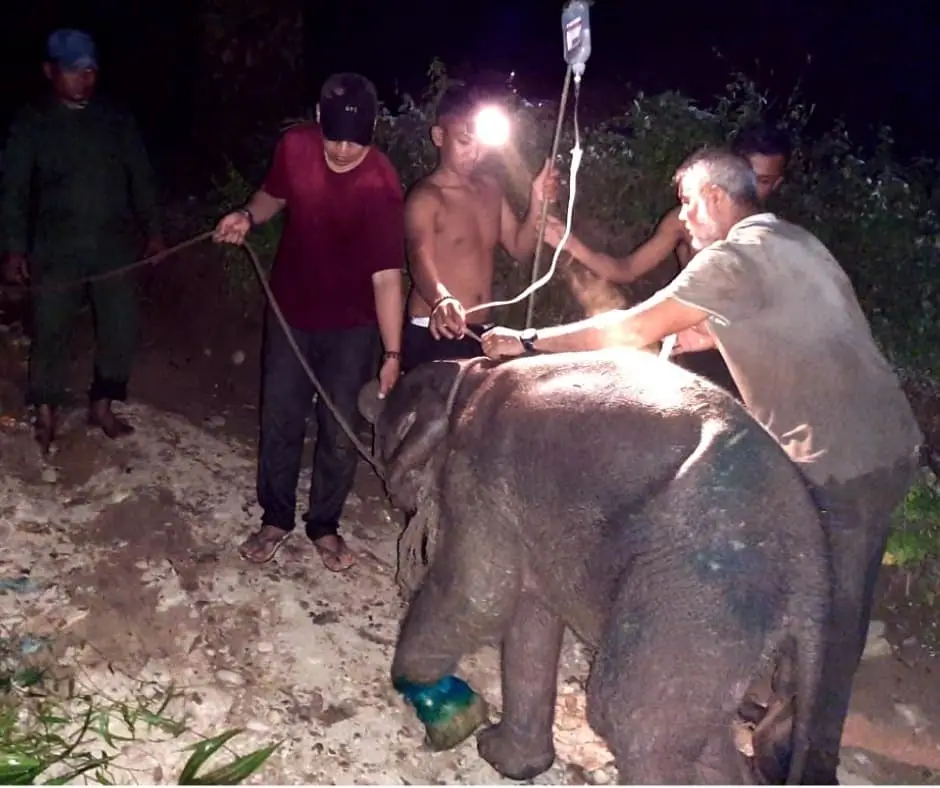
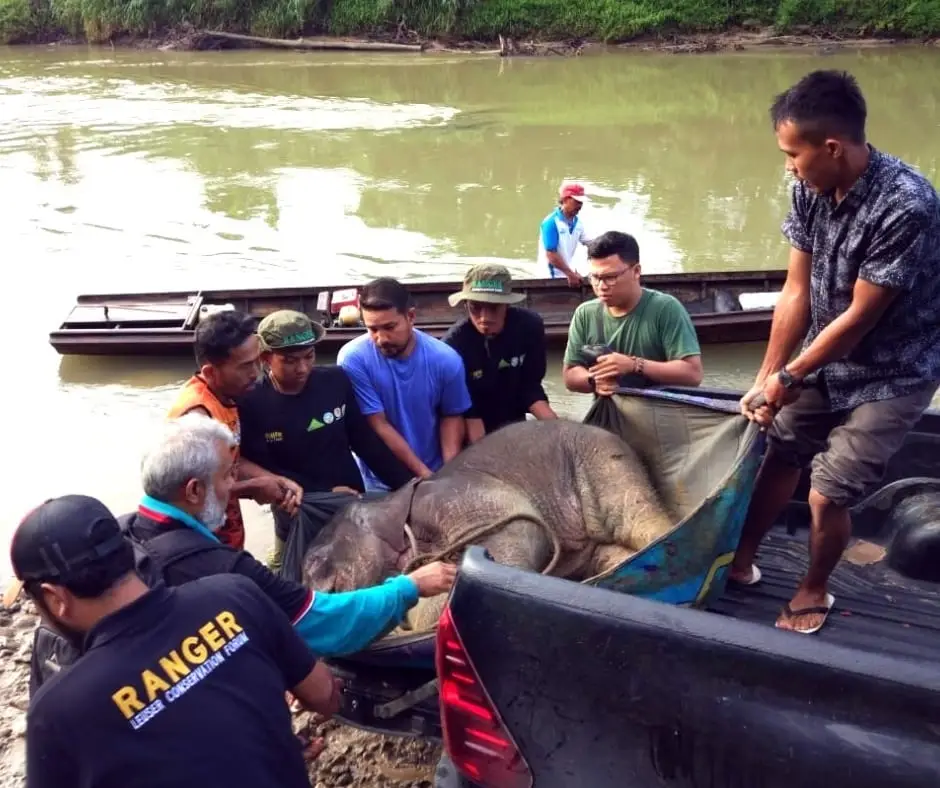
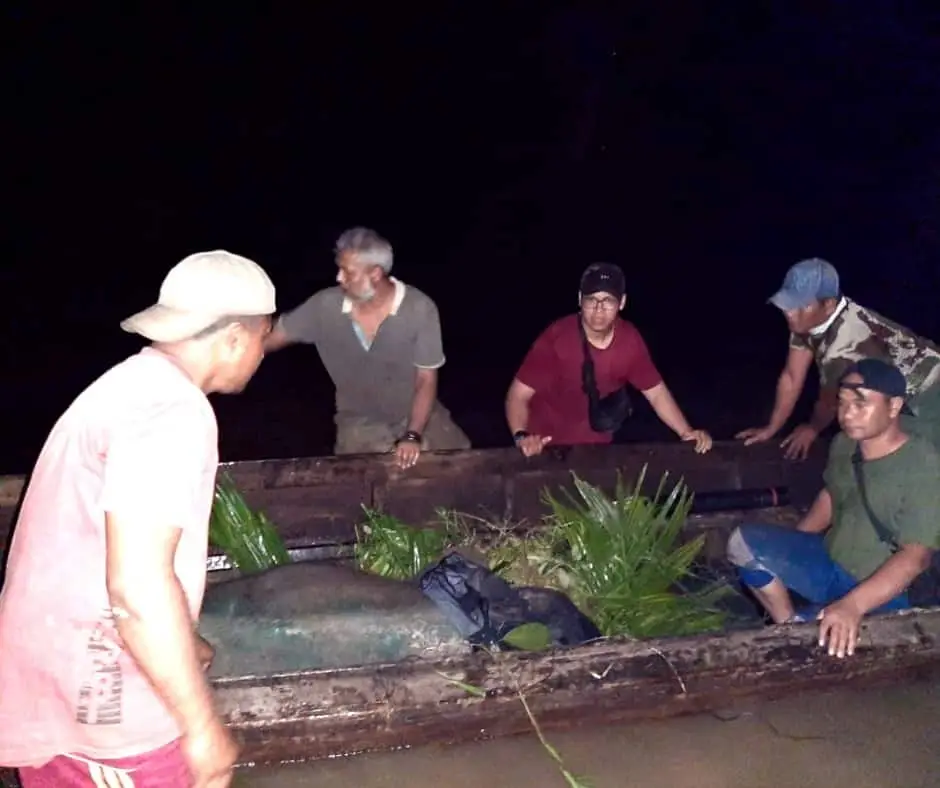
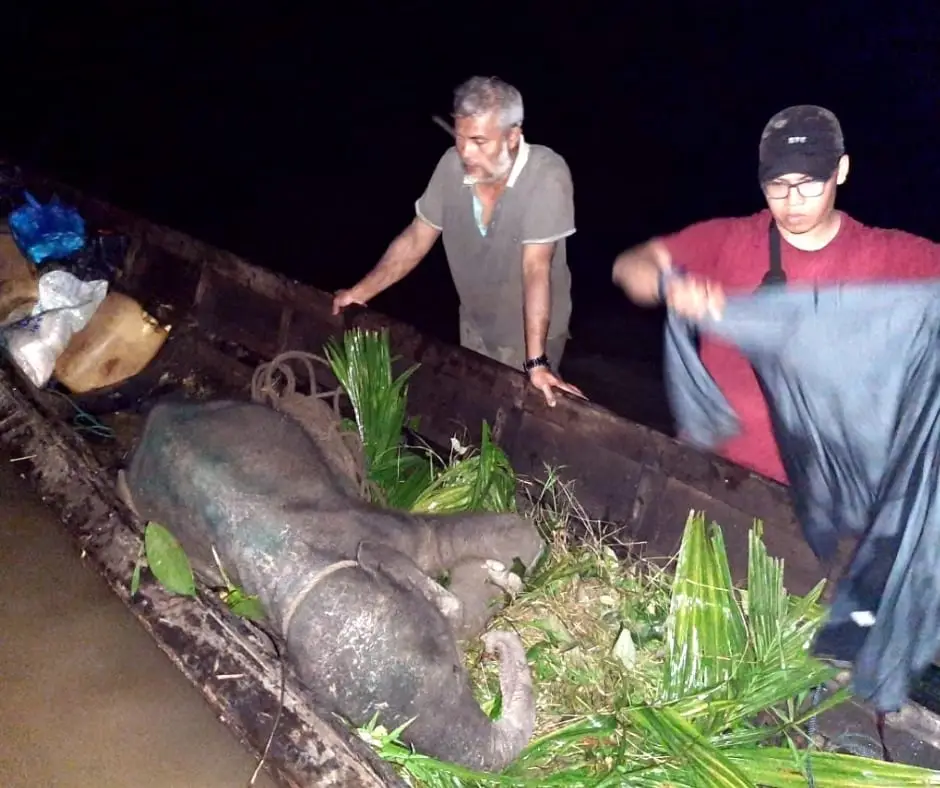
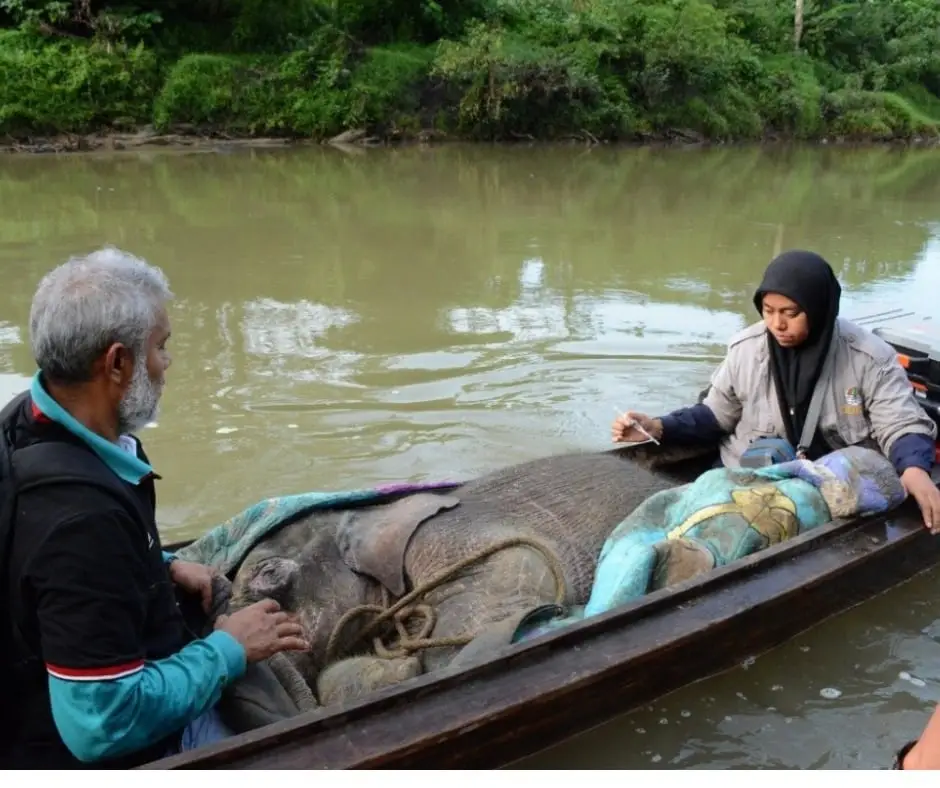
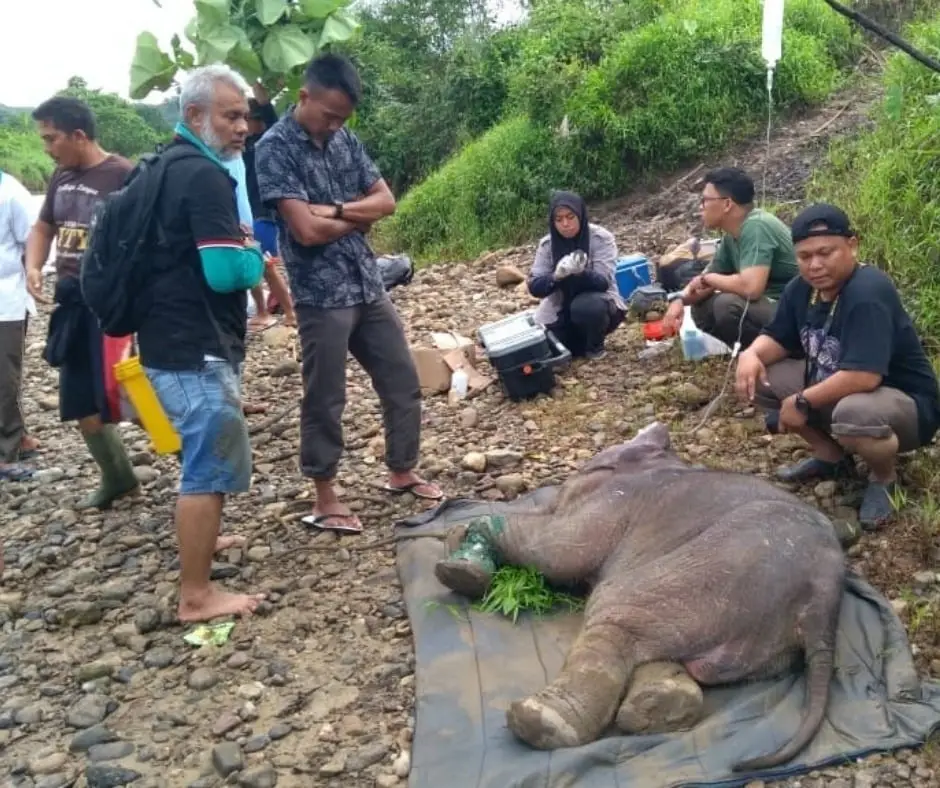
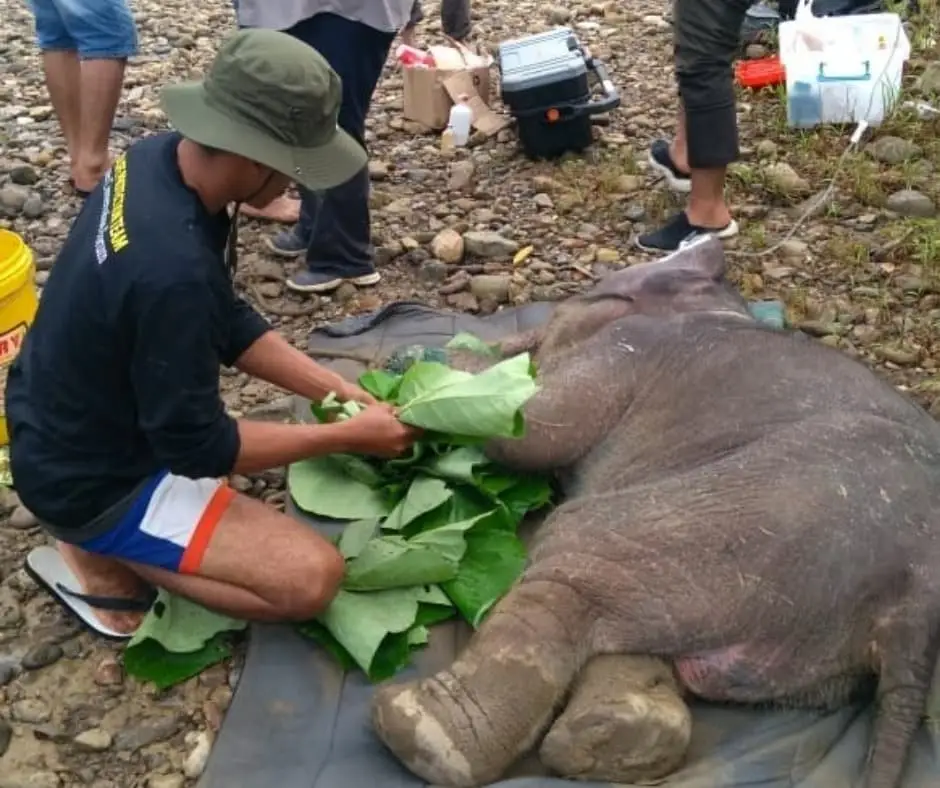









The recovery
With all our willpower, we try our best to ensure the rescue of the elephant.
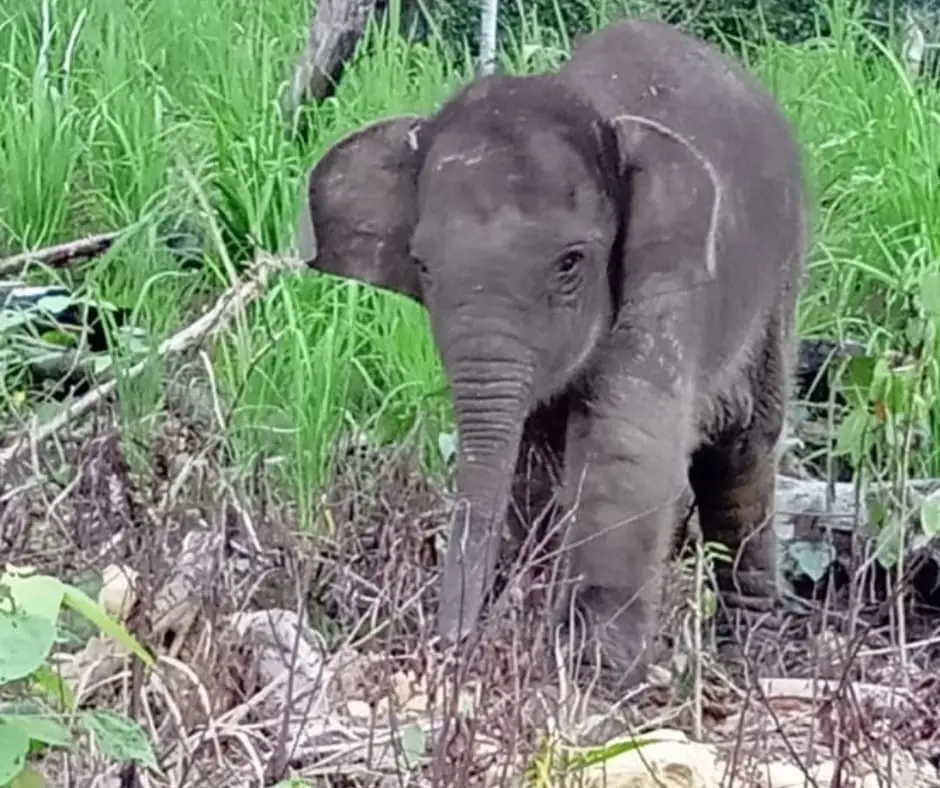
The first weeks was a very difficult time for the elephant to live among humans. But at the very least, she feels comfortable. She is able to sleep surrounded by humans and happy to be fed milk.
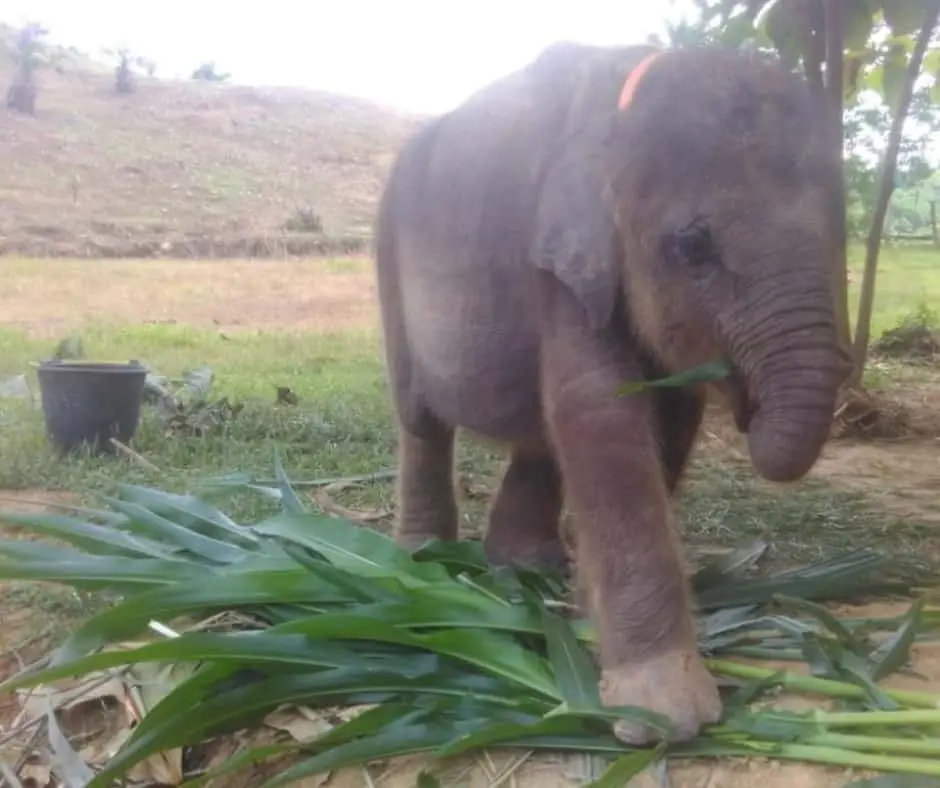
Our staff is on standby monitoring 24 hours, 7 days a week. She is now recovering, socializing with other tame elephants at the camp, and has recently started eating grass as well.
The cute elephant is loved by the team and staff at the camp. It is unthinkable that anyone would injure her. The elephant is later named Salma (an acronym for “Save the Wildlife in Leuser and Aceh Communities” in Bahasa Indonesia).
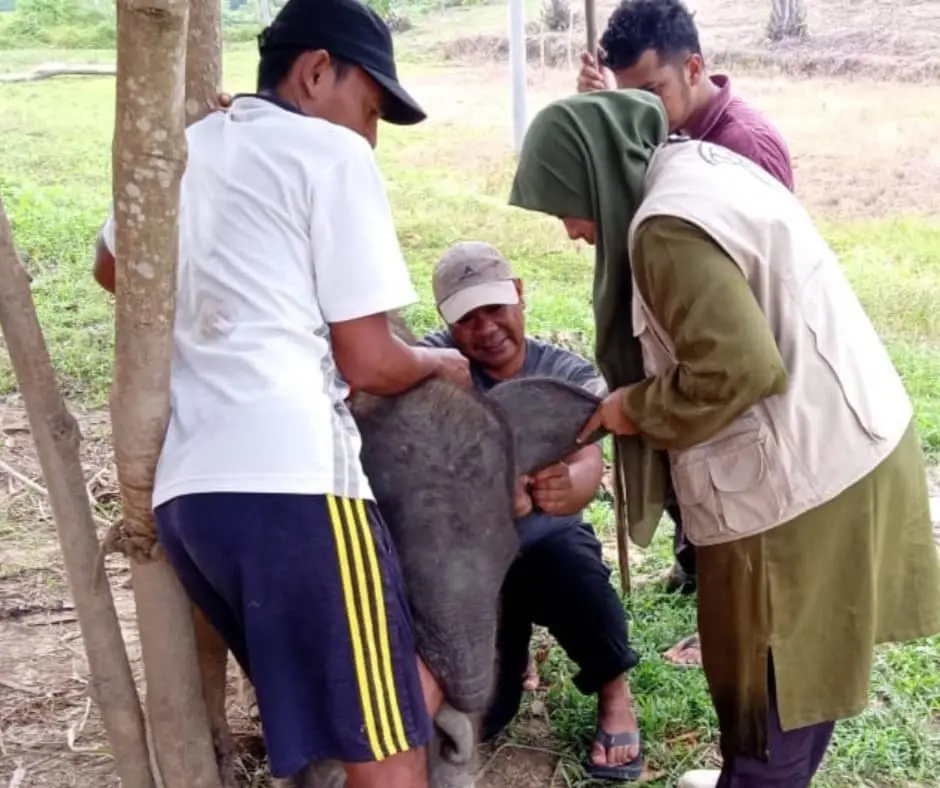






sumatra's wildlife needS A refuge
Help build a connection to the future for the wildlife of Leuser. Take a stand for their last refuge by rescuing this vanishing ecosystem, preventing the loss of biodiversity, and building resilience to fight the impacts of climate change.
ABOUT LEUSER CONSERVATION FORUM (FKL)
Leuser Conservation Forum (FKL) was founded in 2013 with a mission to help save the Leuser Ecosystem in Aceh and North Sumatra Provinces. The Leuser Ecosystem is a 2.6 million hectares expanse of forest rich in biodiversity. Today, FKL deploys 26 units of Wildlife Protection Team across the Leuser Ecosystem in Aceh specifically to treat, rescue elephants and other wildlife injured. With more than 200 people in the field, FKL’s protection unit is the biggest managed by a local NGO in Indonesia.
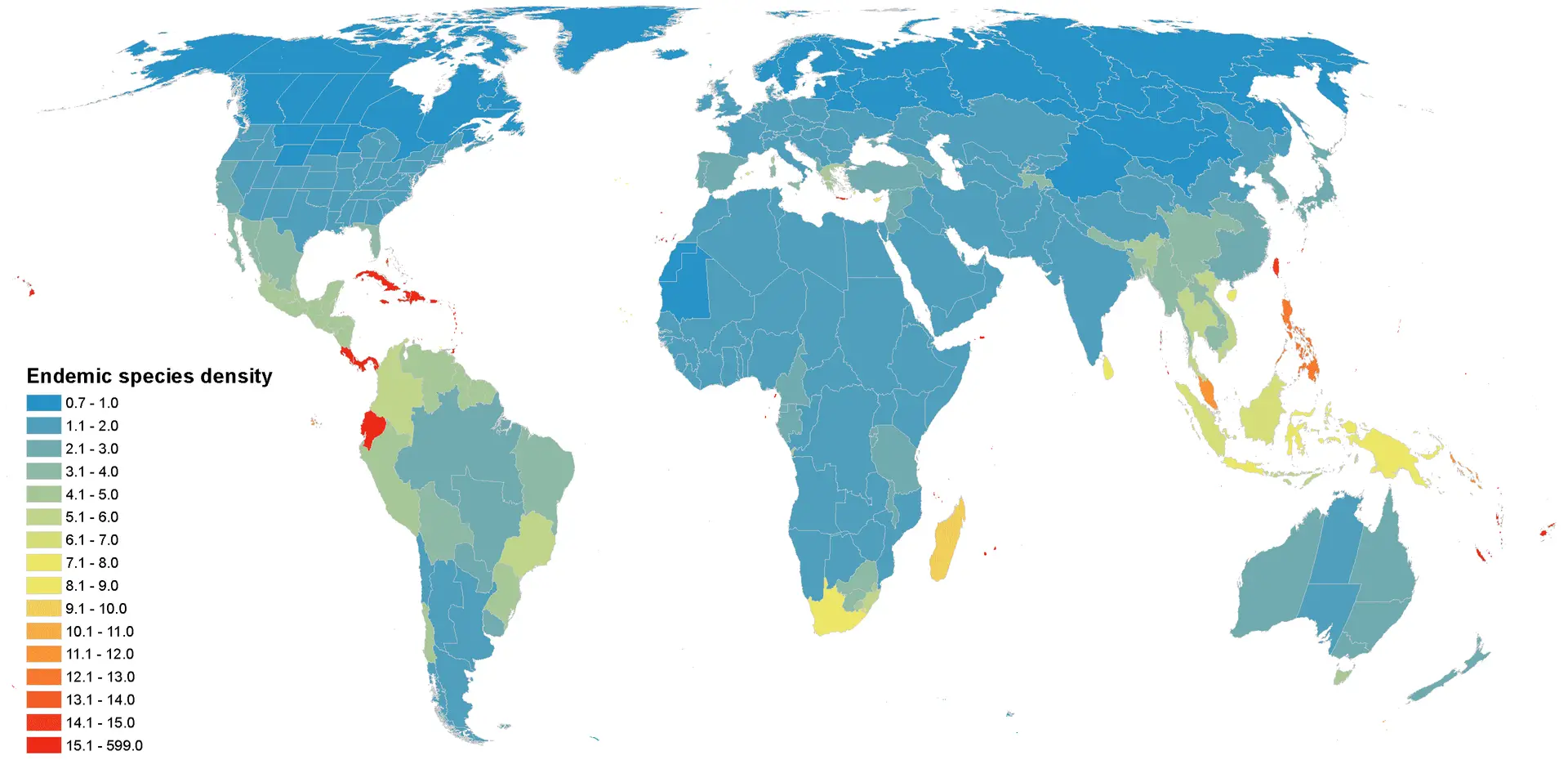
Protecting 20% of Land to Save Two-Thirds of Plant Species
September 5, 2013
You’ve heard the adage, “If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.” But new research by Saving Nature scientists offers an amazing conservation ‘deal’. Backed up by top-flight science and data, it’s too good to pass up. So what is the deal? The new paper, published today in Science, was co-authored by Saving Nature founder Stuart Pimm and Vice President Clinton Jenkins, and by Lucas Joppa of Microsoft Research, who completed his Ph.D. with Pimm.
PROTECTING A FIFTH OF THE WORLD'S LAND TO SAVE TWO-THIRDS OF ALL PLANT SPECIES
The key finding of the paper is that protecting a fifth of the world’s land area will save two-thirds of the world’s endemic plant species. Using the Kew Gardens plant database, the authors looked at the geographical distributions of 110,000 plant species. From this analysis, the researchers identified the smallest set of regions that contain the largest number of plant species.
They discovered that nearly two-thirds of the world’s plants occur in just 17 percent of the world’s land. The bad news is that less than a sixth of that 17 percent is currently protected. “Our study identifies regions of importance. The logical – and very challenging – next step will be to make tactical local decisions within those regions to secure the most critical land for conservation.” Pimm said.

Incorporating years of data, Jenkins created a detailed, color-coded map of Earth. The map illustrates where endemic plants are concentrated. This information helps conservation ecologists, policy makers, and economists to prioritize locations for conservation eorts. Because of ecological food webs, protecting endemic plants not only helps save rare plant species—it helps save dependent species, such as specialist herbivores, epiphytes and so on. “We also mapped small-ranged birds, mammals and amphibians, and found that they are broadly in the same places we show to be priorities for plants,” said Jenkins. “So preserving these lands for plants will benefit many animals, too,” he said.
According to Pimm, to achieve biodiversity conservation goals, the world needs to protect more land than we currently do and much more in key places such as Madagascar, Colombia, and coastal Brazil. These are all places where Saving Nature works.
Saving Nature relies on cutting-edge science to make its conservation decisions. With the limited amount of conservation funding available, we must use the best science to maximize the number of threatened species of wildlife and plants we can save. The report’s findings truly oer conservationists a great deal.
SCIENTIFIC NOTE: The work in Science focused on endemic species of plants. Endemic species exist only in specific places, such as a particular mountain range or forest. Endemic species are typically very rare, because of their limited geographical distribution. Endemic plants are also crucial to ecosystems that support other endangered species and, more broadly, biodiversity. Because they exist only in one place, endemic plants are often hosts for other endemic species that depend on them—insects, animals, and even other plants such as epiphytes.

